Configuring for first use
This section shows you how to configure HCP Terraform or Terraform Enterprise to meet your requirements for delivering IaC services to your internal customers.
Post-installation tasks
An optional step at the end of automated installation of Terraform Enterprise is the creation of the Initial Admin Creation Token(opens in new tab) (IACT), but further initialization tasks complete the setup. There are two viable options for post-provision configuration in Terraform Enterprise: API scripts or using the Terraform Provider. The best practice is to use the Terraform Enterprise provider(opens in new tab) to derive state for the configuration.
SSO and teams
The setup of SSO for HCP Terraform is not covered in detail in this document, as configurations can vary depending on the SAML 2.0-compliant provider used.
- You can find specific instructions for popular identity providers here(opens in new tab).
- For applicable SAML 2.0 documentation, here(opens in new tab).
We recommend automating the creation of teams alongside projects, Stacks, and workspaces using the Terraform Enterprise provider. After creating the initial teams required, automate the addition of users within your strategic IdP platform. By adding a team attribute name (default: MemberOf) attribute within your IdP, you can automatically assign users to the created groups in the SAML configuration. You can find further details here(opens in new tab).
Note: For user accounts used by pipelines, use IsServiceAccount set to true to flag these in SAML. See isserviceaccount(opens in new tab). Create teams in Terraform Enterprise with the exact name of the group in the IdP. Do not create users manually - Terraform Enterprise creates these automatically after it processes the SAML assertion at login.
Connect to a version control system
We recommend connecting HCP Terraform/Terraform Enterprise to your VCS provider to enable workflows for managing modules in the private registry, managing Sentinel or OPA policy-sets, and connecting VCS-backed Stacks and workspaces to VCS repositories.
GitHub app
If using GitHub, the preferred method of VCS connection is a GitHub App, for a number of reasons. A GitHub App is not tied to a specific user, does not require a personal access token, and is safe to set up as a static VCS connection with no need to rotate tokens. A GitHub App connects Terraform to GitHub, but confers no access permissions itself. Instead, the following elements govern access to repositories.
- The GitHub organization(s) housing the GitHub App.
- Individual GitHub user permissions (to use the GitHub App, Terraform users must authorize it with their GitHub credentials).
See GitHub's documentation(opens in new tab) for more detail.
Terraform Enterprise supports a single site-wide GitHub App, shared across all Terraform Enterprise organizations. To use it, create and configure it(opens in new tab) using a site administrator account.
Choose the appropriate level of visibility for your GitHub App from the following list.
- If you only have one GitHub organization, configure your GitHub App as private.
- If you have multiple organizations under the same GitHub Enterprise, create the App under your enterprise account(opens in new tab) (at the time of writing, this feature is in public preview).
- If you need access to repositories across multiple GitHub organizations, configure your GitHub App as public but do not list it on GitHub's marketplace.
HCP Terraform has a pre-configured public GitHub app(opens in new tab) which you can install in any GitHub organization(s) as required.
OAuth
For providers other than GitHub, authorize VCS connections using OAuth within each Terraform Enterprise organization. Do this using a manual UI workflow(opens in new tab) using an ID and secret from the VCS, or automated using the HCP Terraform and Terraform Enterprise provider(opens in new tab) using an access token from the respective VCS account. As with all static tokens, it is good practice to rotate this periodically.
OAuth authorizes Terraform Enterprise to act as a specific user or account on the VCS. The permissions of that account govern the access Terraform has to VCS organizations and repositories. For simplicity, we recommend setting up a single OAuth connection per VCS provider in each Terraform Enterprise organization. Use a service account with access to all IaC and policy-as-code repositories, to avoid any dependency on individual employee accounts.
If you require a more granular or least-privilege permissions model, you can create multiple OAuth VCS connections, each mapping a subset of VCS repositories to a subset of Terraform projects. In this case it would be a function of a landing-zone module to create these OAuth connections and project mappings(opens in new tab) on demand whenever a new project onboards.
Audit
In HCP Terraform only, the Audit Trails API(opens in new tab) provides access to audit events. We recommend Terraform Enterprise customers forward logs(opens in new tab) for monitoring and auditing purposes. See the section on observability for more details. Include audit, logging, and monitoring in the target architecture for the delivery of your project. Do not wait until after go-live to implement observability.
HCP Terraform agents
Pools of HCP Terraform agents allow HCP Terraform and Terraform Enterprise to communicate with isolated APIs in discrete network segments such as those on premise. We recommend defining agent pools and assigning Stacks and workspaces to them using the Terraform Enterprise provider as appropriate. This improves the availability of your on-premise APIs and allows for configuration of network hardware, internal VCS, CI/CD systems and so on, using IaC. This improves the return on investment of HCP Terraform and Terraform Enterprise.
You may choose to run multiple agents within your network, up to the organization's purchased agent limit (which only affects HCP Terraform customers; there is no such limit for Terraform Enterprise customers). Each agent process runs a single Terraform run at a time. Multiple agent processes can be concurrently run on a single instance, license limit permitting.
We strongly recommend reading the HCP Terraform agent documentation(opens in new tab) as part of your implementation planning.
Compatibility
Agents support Terraform versions 0.12 and later only. Workspaces configured to use Terraform versions below 0.12 cannot select the agent-based execution mode.
When running Terraform Enterprise, consult the release notes(opens in new tab) for agent version restrictions for your target Terraform Enterprise version and also the HashiCorp considerations for HCP Terraform agents on Terraform Enterprise(opens in new tab).
Operational considerations
The agent runs in the foreground as a long-running process that continuously polls for workloads from HCP Terraform. An agent process may stop due to a variety of reasons. We strongly recommend pairing the agent with a process supervisor to ensure that it automatically restarts in case of an error. On a Linux host, do this using a systemd manifest such as the one below.
[Unit]
Description="HashiCorp HCP Terraform Agent"
Documentation="https://www.terraform.io/cloud-docs/agents"
Requires=network-online.target
After=network-online.target
[Service]
Type=Simple
User=tfcagent
Group=tfcagent
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/tfc-agent
KillMode=process
KillSignal=SIGINT
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5
EnvironmentFile=-/etc/sysconfig/tfc-agent
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
If using HCP Terraform agents in containers, use single-execution mode(opens in new tab) to ensure your agent only runs a single workload and guarantees a clean working environment for every run.
Upgrading HCP Terraform agents
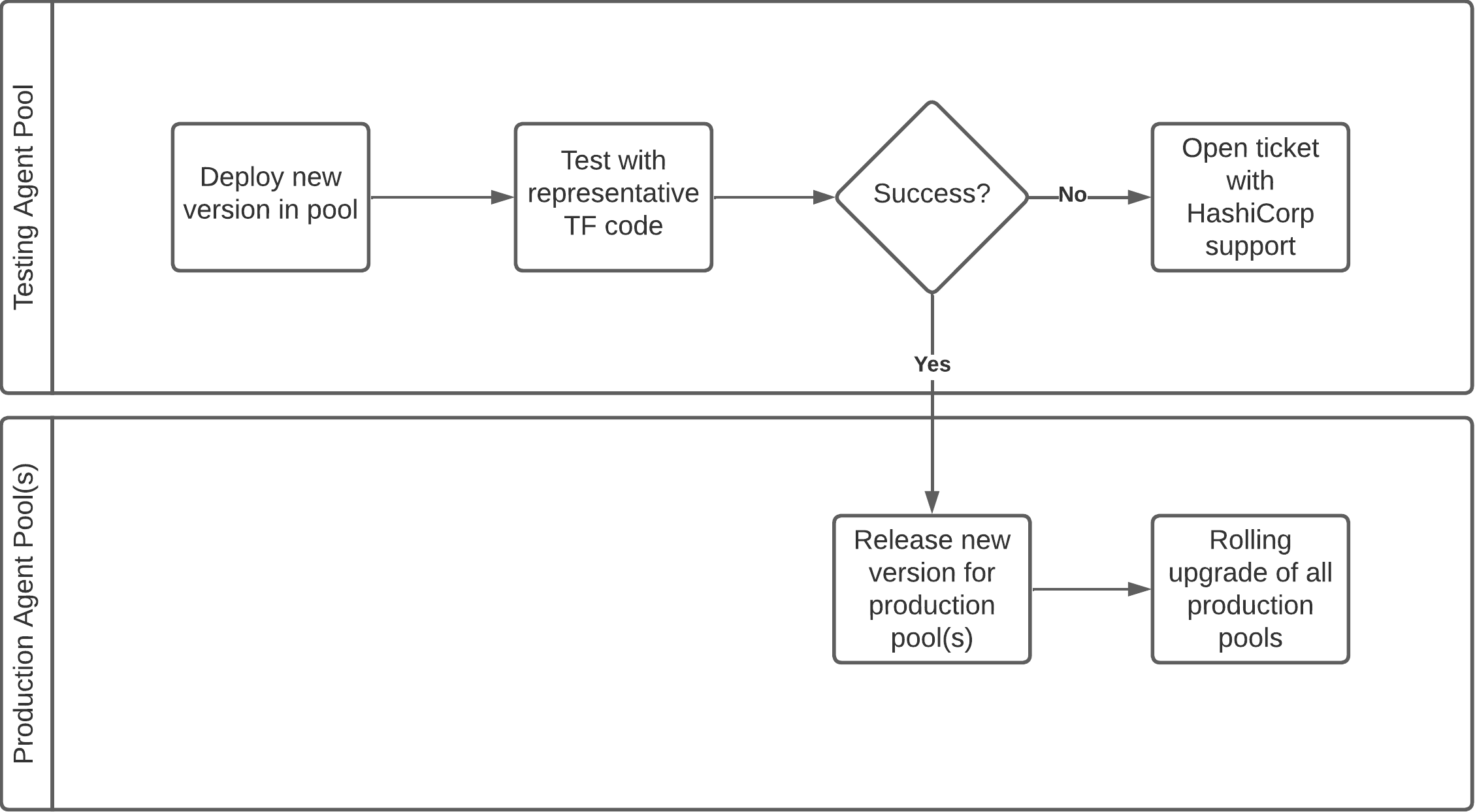
When HashiCorp releases a new version of Terraform Enterprise, we test it against the most current HCP Terraform agent version. Should you need to upgrade your HCP Terraform agent version, we recommend testing the new version in a separate agent pool before rolling it out to your main agent pool(s). Use the platform team's dedicated HCP Terraform organization or Terraform Enterprise instance for this.
When considering use of HCP Terraform agents, do not skip testing, and we suggest that the extent of the testing effort must match the extent of the change. Patches and minor changes require little testing, while major changes require more extensive tests.
The diagram below illustrates our recommended roll-out approach for a new HCP Terraform agent version: