Overview
Autopilot is a set of features to allow for automatic operator-friendly management of Nomad servers. It includes automated upgrades, monitoring the state of the Raft cluster, and stable server introduction. This allows the Nomad upgrade process to be simplified.
See the Autopilot tutorial(opens in new tab) page for a basic tutorial and see below for more detail.
Prerequisites
- Only if you are running Nomad 1.3 or older, set
raft_protocolto 3 on all server nodes because the default raft versions were less than 2. This may also apply if you have upgraded from an older version, but never upgradedraft_protocolto 3. If you are running an older Nomad version with the parameter set to 2 or lower, then work to upgrade Nomad Enterprise. Refer to the Raft Protocol Version Compatibility(opens in new tab) documentation for more details. - Add
autopilot{}block and its parameters to the server node configuration before bootstrapping the cluster. Use thenomad operator autopilot set-configcommand as an alternative, or use the/v1/operator/autopilot/configurationAPI endpoint. Refer to the Autopilot documentation(opens in new tab) for more information on how to enable Autopilot.
We recommend you to have a build pipeline with Packer to create golden images, deploy the machines with Terraform, and a configuration management tool such as Ansible to perform any OS level operations after the VM provisioning.
Use the pipeline to deploy Nomad VMs with the new Nomad version or to do any changes to the OS or Nomad configuration. See the Using Terraform to Configure Nomad section for more details and recommendations on the deployment process.
Example pipeline
Below is an example pipeline of what the upgrade process may look like with Autopilot, Packer, and HCP Terraform.
- Packer builds a new Nomad Enterprise machine image and stores it at an image registry. This example shows AWS EC2 AMI, but the same principles apply for vSphere Content Library, Azure Compute Gallery.
- HCP Terraform uses a new workspace to deploy a new set of Nomad server VMs.
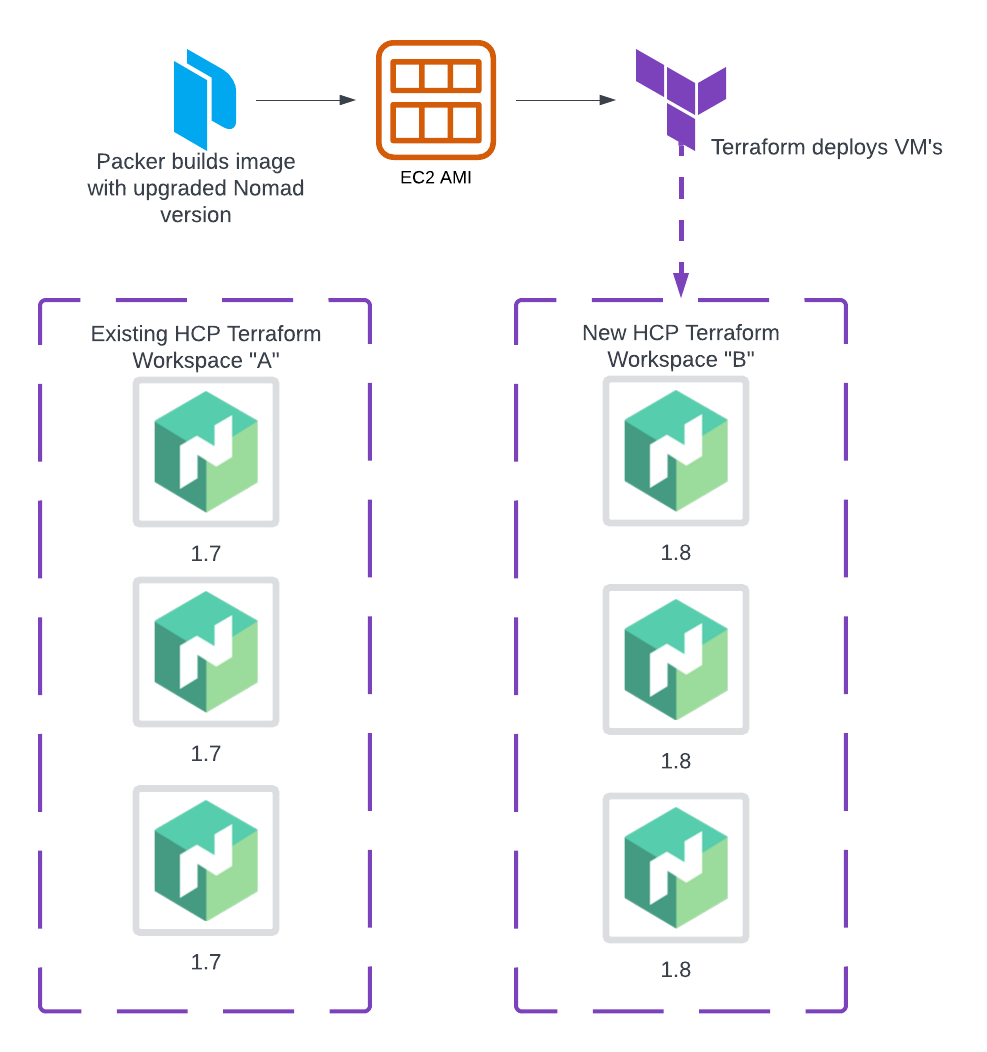 Figure 1: Terraform uses a new workspace to deploy a new set of Nomad servers.
Figure 1: Terraform uses a new workspace to deploy a new set of Nomad servers.
- The new 1.8 nodes are joining the 1.7 cluster.
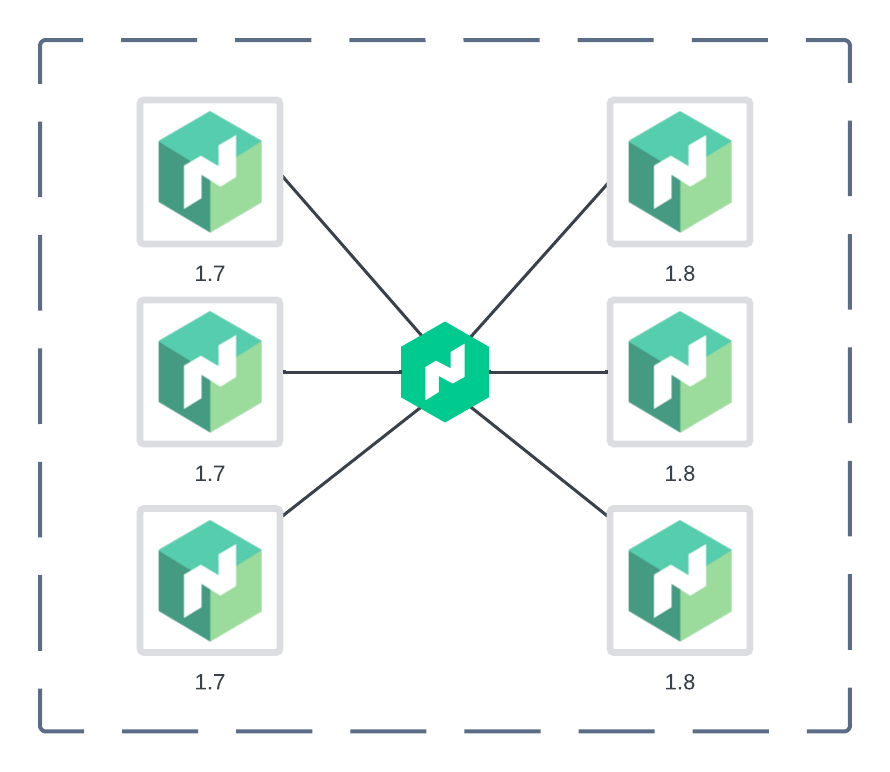 Figure 2: The new nodes are joining the cluster.
Figure 2: The new nodes are joining the cluster.
- Autopilot then automatically demotes the old server nodes to non-voting members so they are no longer participating in the quorum.
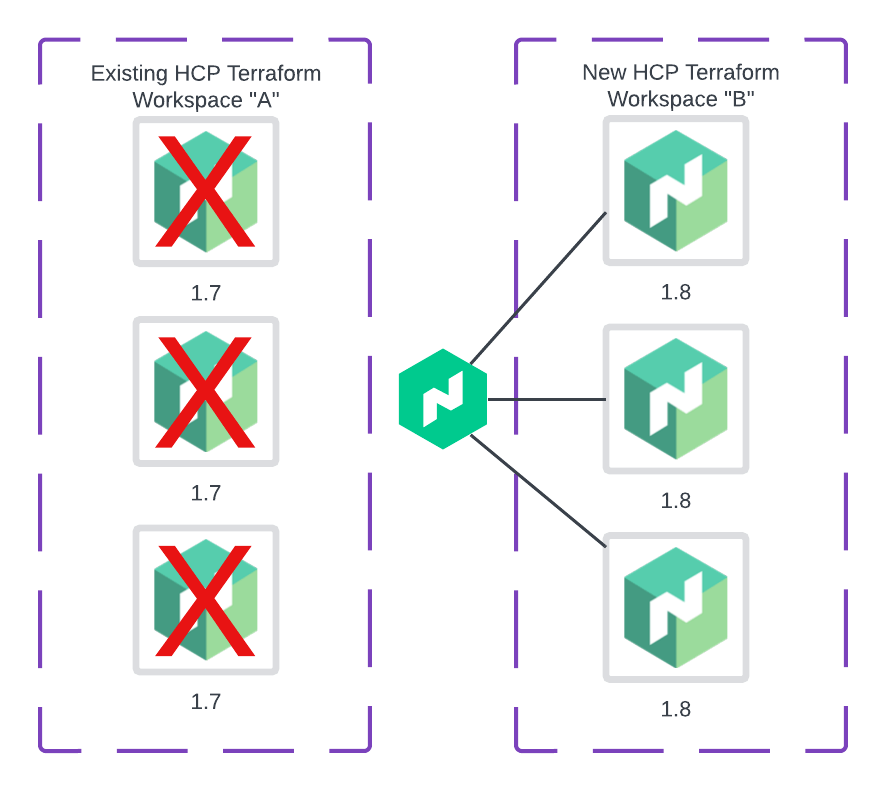 Figure 3: Autopilot automatically demotes the old server nodes.
Figure 3: Autopilot automatically demotes the old server nodes.
Run nomad operator raft list-peers to confirm the Nomad nodes from Workspace A does not have a leader and are not set to voting members. Once you confirmed the Nomad instances deployed from Workspace A are non-voting, run terraform destroy to remove the old instances.
Autopilot recommended configuration options
Cleanup dead server
The cleanup_dead_servers parameter ensures that dead servers are automatically removed from the cluster. This is crucial for maintaining a healthy cluster state.
autopilot {
cleanup_dead_servers = true
}
Last contact threshold
The last_contact_threshold parameter defines the maximum allowed time since the last contact with a server before Nomad Enterprise marks it unhealthy.
autopilot {
last_contact_threshold = "200ms"
}
Server stabilization time
The server_stabilization_time parameter defines the time a server must be stable before Nomad Enterprise marks it as healthy.
autopilot {
server_stabilization_time = "10s"
}
Max trailing logs
The max_trailing_logs parameter specifies the maximum number of log entries a server can trail behind the leader before it is considered unhealthy.
autopilot {
max_trailing_logs = 250
}
Server stabilization time
The server_stabilization_time parameter specifies the minimum duration a server must be stable before Nomad Enterprise adds it to the cluster. The appropriate value depends on your server hardware and startup time.
autopilot {
server_stabilization_time = "10s"
}
Enable redundancy zones
The enable_redundancy_zones parameter allows you to enable redundancy zones, which improves the fault tolerance of your Nomad cluster by distributing voting servers across distinct failure domains. We recommend naming the redundancy_zone in your server configuration the same as the underlying availability zone.
autopilot {
enable_redundancy_zones = true
}
Disable upgrade migration
Set the disable_upgrade_migration parameter to false to allow automatic upgrades.
autopilot {
disable_upgrade_migration = false
}
Disable upgrade migration and enable custom upgrades
disable_upgrade_migration and enable_custom_upgrades
By default, Nomad Enterprise enables Autopilot's upgrade migration strategy, and disables custom upgrades.
This allows Autopilot to automatically manage the upgrade process. If you have specific upgrade requirements or want to manually control the upgrade process due to just configuration changes without a newer version, you can set disable_upgrade_migration to true and enable_custom_upgrades to true.
This allows you to implement your own upgrade logic.
For most cases, we recommend to leverage Autopilot's default upgrade migration strategy for a seamless and automated upgrade experience.
If you choose to enable custom upgrades, ensure that you have upgrade_version set to your specific versioning semantics to allow you to increment the version tag on future images.